
TAILORED WITH TECHNOLOGY
How fintech is fuelling growth

Technological disruption is becoming more widespread. Digitisation, one type of this disruption, is impacting businesses in myriad unanticipated ways, enabling them to become more agile and flexible.
With fintech—the provision of financial services via various forms of technology — companies are being equipped with the necessary tools and services to grow and expand internationally.
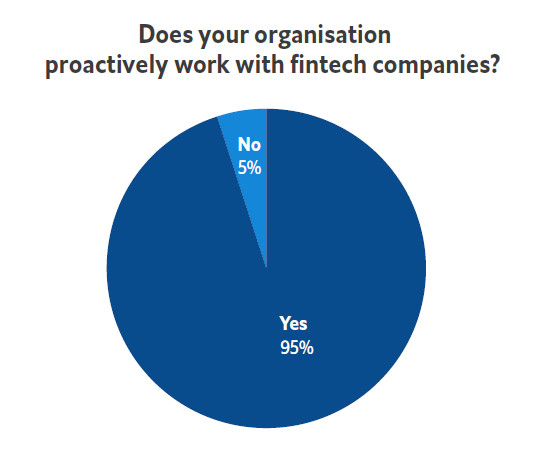
In our survey of more than 750 executives across eight countries, we found 95 percent of companies in the financial services sector are reaping major benefits from deploying fintech services.
Financial services firms are not the only beneficiaries, however. “Companies across sectors from ride-hailing, logistics, agriculture (agri-tech), and healthcare (health-tech), to fashion, hospitality, and insurance (insuretech) are being impacted by fintech solutions with many companies looking to integrate and or leverage these technologies and platforms to catalyse growth,” says Geoffery Prentice, co-founder of Oriente, a Hong Kong-headquartered financial services and technology company.
Additionally, by driving change in the financial services sector, many fintech companies are helping other sectors in the process, says Carl Wegner, Asia Pacific head of R3, an enterprise blockchain software provider.
“Fintechs which help with organising of payments, for example, will bring benefits to suppliers across a whole range of sectors as their cash flow is made more efficient.”
Making transacting easier
One critical issue fintech is addressing is the long-standing problem with payments. Traditional payment processes are cumbersome and can drain a company’s resources and finances. This is true of domestic payments to suppliers and vendors and even more so in the case of cross-border payments.
Mr Prentice says fintech helps in two main ways—reach and network—through enhancing “mobility and agility”.
Fintech solutions today are enabling local businesses to streamline and integrate payments systems that enable easier and cheaper cross border transactions.
Now even smaller companies are able to sell their goods and services in markets where they once hadn’t been able to venture and without having to invest in physical infrastructure, such as office space.
Customers can now even pay for products and services through mobile wallets and other methods, meaning without directly accessing their bank accounts.
This streamlining has enhanced customer satisfaction levels and boosted retention rates for firms. Over-the-top media companies such as Netflix are a working example of this model.
For example, the use of blockchain, a distributed ledger technology, is enabling businesses to reach new customers and to expand to overseas locations. Mr Wegner says that “[by] using blockchain, financial institutions can send and settle payments in seconds and for a fraction of the cost of traditional bank transfers.” Payment processes have become faster, more secure and user-friendly as a result, helping increase revenue margins.

“fintech helps in two main ways—reach and network—through enhancing “mobility and agility.”
Integrating supply chain solutions
An efficient supply chain is an integral part of operations for most international firms. They constantly face short-term liquidity needs that banks are often unable or unwilling to finance, making it necessary for them to assess alternatives to manage their working capital.
Fintechs are increasingly making life easier for both buyers and sellers by providing greater liquidity and consistency in terms of the timing of payments. Whereas in the past, suppliers often had to wait for months to receive their payments, now they have a wide array of faster funding solutions for customers, including alternative invoice discounting, supply chain finance and factoring.
Some firms also combine these with inventory management and other related services. It isn’t just smaller companies that benefit from fintech. Multinationals are using fintech — particularly blockchain technology — to “track and trace” products, making their supply chains more efficient. They are also using it to improve customer intelligence.
Mr Prentice says fintech gives companies the ability to act in real-time to changes in demand.
“Fintech is a data-centric model and is becoming instrumental in helping multinational companies make more informed decisions in real-time based on big-data analytics,” he says.
The Economist Intelligence Unit, commissioned by ANZ institutional, surveyed over 750 executives across the technology, resources, energy and infrastructure, food, beverages and agriculture and financial services industries in seven key markets: Australia, China, Hong Kong, New Zealand, Singapore, United Kingdom, United States and India.
The survey, conducted in the spring and summer of 2019, was designed to capture insight into the role of technology in corporate growth, sustainability and the macro-economy.
Three reports were written based on insights from the data. You can read the first report HERE.
Filling a void
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are the driving force of most economies globally, yet can sometimes struggle to access traditional financing solutions. Fintechs are playing a crucial role in filling this funding gap, helping both long-term financing requirements as well as working capital.
Fintech organisations are using tools enabled by artificial intelligence and big data to gauge credit-worthiness, creating a reliable credit history for previously unfinanced SMEs. This, coupled with low overheads, allows fintechs to lend to micro, small and medium enterprises more quickly and at lower costs.
This is instrumental in supporting these companies’ growth ambitions. In Southeast Asia, for example, thousands of small companies’ growth is inhibited due to capital constraints. Ride-hailing apps Go-Jek and Grab are swiftly moving into the fintech space to fill the funding void for smaller firms.
Separately, payment processing fintech companies “can show businesses consumer patterns and provide data about interests, wants and needs,” says Mr Prentice. Small businesses can use this data to improve their marketing for leads and current customers, putting them closer to on the same footing as their larger competitors.
Besides financing solutions, fintechs enable a streamlining of processes, which benefits small and large companies alike. According to Mr Wegner, large companies are likely to face structural challenges which can impact their ability to expand.
“A conglomerate may find itself with many fragmented processes that operate in silo due to the size [of the firm], which in turn affects efficiency and connectivity across the wider business,” he says.
Blockchain can help overcome this by serving as what he calls a “single source of truth”, or a singular model, that can be adopted and replicated across all parts of business. For large companies, achieving this kind of universality across various moving parts of a business can be the key to unlocking scale, Mr Wegner says.
What the future holds
Fintech is helping companies overcome funding and size constraints by providing them with tools and solutions that are enabling them to do things faster, better and in a more cost-effective manner.
The financial services sector is naturally ahead of the curve at this point given the direct benefits fintech brings it, but fintech solutions are increasingly useful across other sectors, too. Traditional companies that earlier resisted technology adoption, are also partnering with fintechs to address pain points in their business. And some are even funding them as they look to mitigate constraints.
This publication is published by Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited ABN 11 005 357 522 (“ANZBGL”) in Australia. This publication is intended as thought-leadership material. It is not published with the intention of providing any direct or indirect recommendations relating to any financial product, asset class or trading strategy. The information in this publication is not intended to influence any person to make a decision in relation to a financial product or class of financial products. It is general in nature and does not take account of the circumstances of any individual or class of individuals. Nothing in this publication constitutes a recommendation, solicitation or offer by ANZBGL or its branches or subsidiaries (collectively “ANZ”) to you to acquire a product or service, or an offer by ANZ to provide you with other products or services. All information contained in this publication is based on information available at the time of publication. While this publication has been prepared in good faith, no representation, warranty, assurance or undertaking is or will be made, and no responsibility or liability is or will be accepted by ANZ in relation to the accuracy or completeness of this publication or the use of information contained in this publication. ANZ does not provide any financial, investment, legal or taxation advice in connection with this publication.





